Vaultrice Security Guide
An in-depth look at our layered security model, designed to give you the flexibility and control to match your application's specific security requirements.
A Layered Approach to Security
Security at Vaultrice is not a single feature but a series of layers you can apply to match your application's needs. Each level builds upon the last, allowing you to move from basic protection to maximum, end-to-end confidentiality. This approach ensures that you have the tools to secure your application, from simple projects to those handling highly sensitive information.
Explore the SDK authentication methods available for your application.
Security Levels at a Glance
Each Security Level includes all features from the levels below it. Higher levels inherit and build upon previous security protections.
SF 0| Security Level | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
Level 0 | Public data & prototypes | |
Level 1 | Controlled access & internal apps | |
Level 2 | Enhanced server-side data protection | |
Level 3 | Maximum confidentiality & sensitive data |
This approach ensures that you have the tools to secure your application, from simple projects to those handling highly sensitive information.
Transport + Default At-Rest Encryption
What It Is
All communication between your application and Vaultrice is encrypted in transit using TLS (HTTPS). Additionally, any data stored on the backend infrastructure is automatically encrypted at rest. This protects against network eavesdropping and provides baseline data protection.
Best For
Public data, proofs-of-concept, or any application where the data itself is not sensitive or personally identifiable.
Configuration
Implementation
No special code is required.
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
// Standard initialization provides SF 0 security by default.
// All communication is encrypted in transit (HTTPS)
// All stored data is encrypted at rest automatically
const nls = new NonLocalStorage({
projectId: 'your-project-id',
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
apiSecret: 'your-api-secret'
}, 'my-public-object-id');
await nls.setItem('page_visits', 150);Securing Client-Side Applications
Using the SDK in the browser requires a careful strategy. Vaultrice provides three core features that work together to secure your application. API Key Restriction (SF1) acts as a "perimeter defense" for your credentials. Object ID Signature Verification (SF2) controls which rooms a user can access. And User Identity Verification (SF2 (b)) proves who a user is within that room.
Restrict API Keys
What It Is
Allows you to lock down an API key's permissions by IP address, browser origin (domain), or to read-only/write-only operations. This ensures that even if your API key is exposed, it can only be used from your application's domain.
Best For
All production applications. This is the essential first step to prevent stolen credentials from being used on other websites.
Configuration
In the "API Keys" section of the Management UI, you can add restrictions for "Origins" or "IPs" or "Mode" when editing an API key.
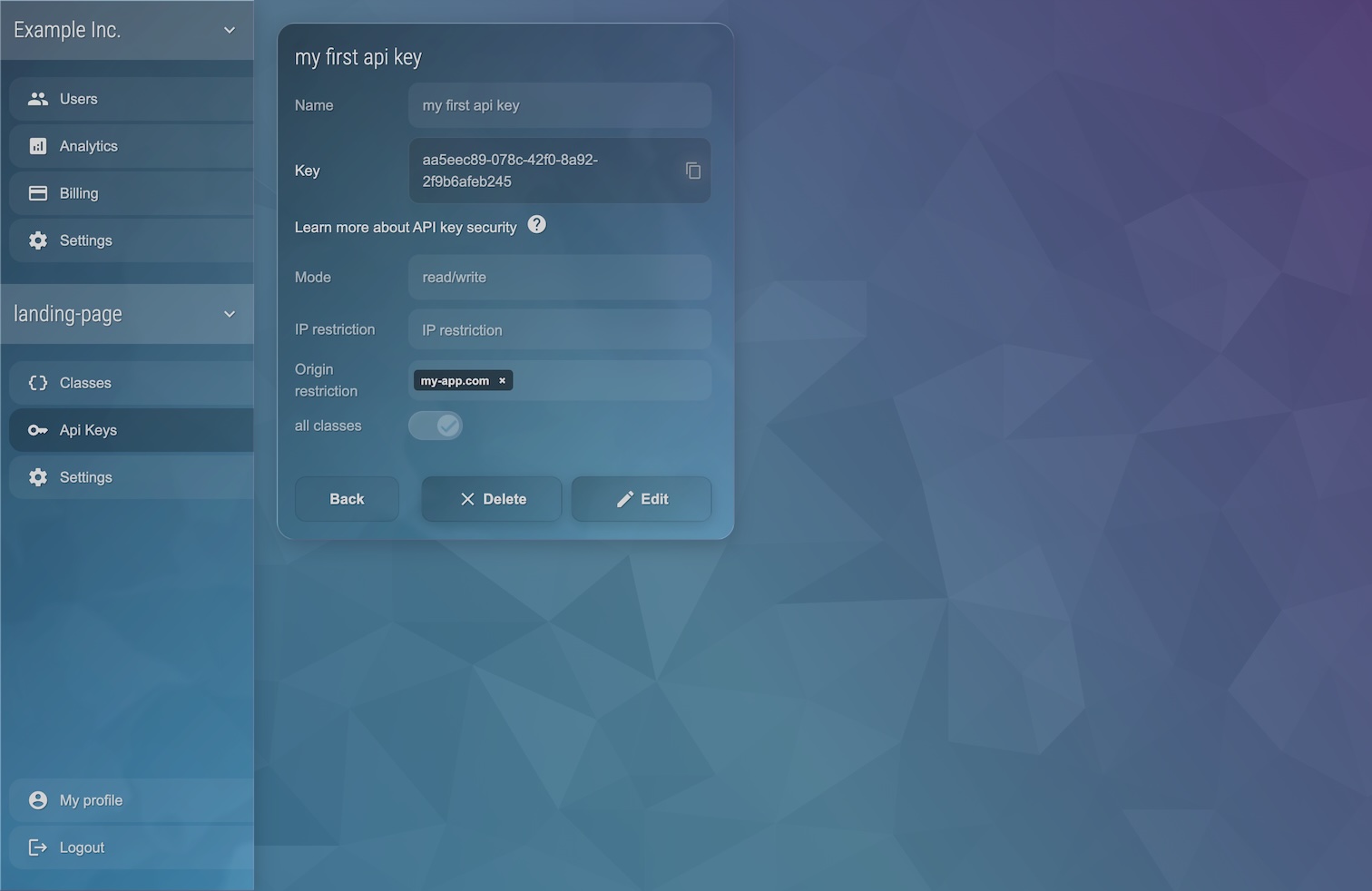
Implementation
No special code is needed in the SDK. The restrictions are enforced by the Vaultrice backend.
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
// This API key has been restricted to "https://your-app.com" in the UI.
// Even if someone steals this key, they cannot use it from another domain.
const nls = new NonLocalStorage({
projectId: 'your-project-id',
apiKey: 'restricted-api-key', // Only works on your domain
apiSecret: 'your-api-secret'
}, 'my-object-id');
// This request will be rejected if made from any other domain
await nls.setItem('user_data', 'secure');Object ID Signature Verification
What It Is
Ensures your backend only interacts with data objects whose IDs have been authorized by your own server. Your server signs an objectId, and the Vaultrice API verifies this signature on every request. This prevents a malicious user on your website from guessing object IDs and accessing data they are not authorized for.
Best For
All multi-user applications. This is crucial to prevent one user from accessing another user's data, even if they are on your website.
Configuration
In the "Classes" settings, enable "ID Signature Verification". You must configure the signature settings, which includes the public key and algorithm configuration.
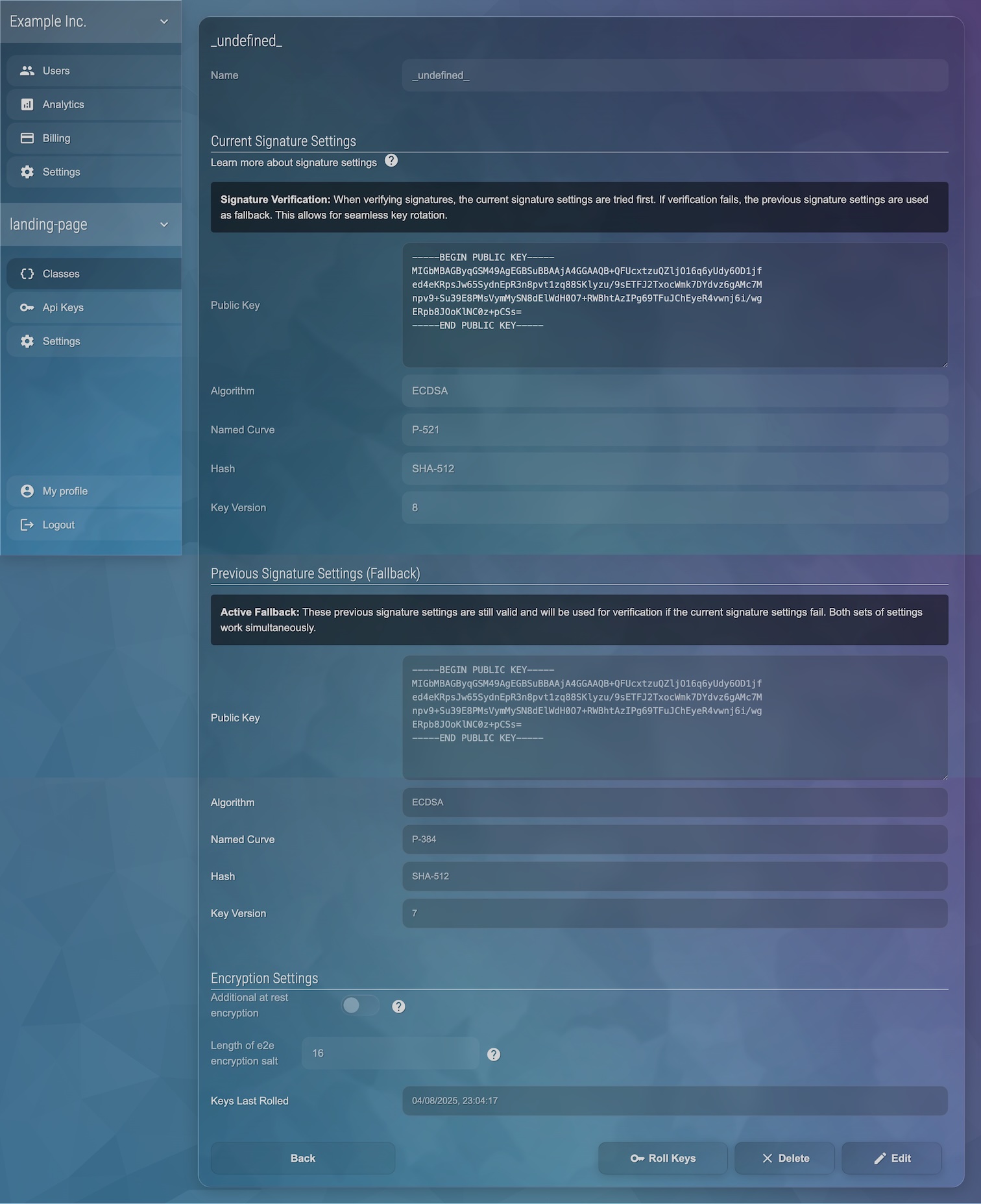
Implementation
Your client application must get a signature from your backend before initializing the SDK.
// On your trusted backend server
const objectId = 'user-profile-12345';
const keyVersion = 2;
// You implement this signing logic using your private key
const signature = signDataWithYourPrivateKey(objectId, keyVersion);
// Send the objectId, signature, and keyVersion to your client
return { objectId, signature, keyVersion };
// --- In Your Client-Side SDK ---
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
// Get signature from your backend
const { objectId, signature, keyVersion } = await fetchSignatureForUser();
// Initialize the SDK with the signature from your backend
const nls = new NonLocalStorage(credentials, {
id: objectId,
idSignature: signature,
idSignatureKeyVersion: keyVersion
});
// The Vaultrice API will now REJECT this request if the signature is invalid,
// even if the API key is correct.
await nls.setItem('username', 'Ada');User Identity Verification
What It Is
Verifies the identity of a user joining a presence channel or sending a message. This ensures that the user data (like userId, name, etc.) associated with presence and messages is authentic and has been authorized by your backend, preventing users from spoofing their identity.
Best For
All multi-user applications where you need to guarantee the identity of participants in a shared session. This is essential for secure chat rooms, collaborative editors, or any application where messages and presence events must be trusted.
Configuration
In the "Classes" settings, under "Presence User Verification," select either "Verify User ID with Signature" or "Verify Payload with JWT" and configure your public key(s).
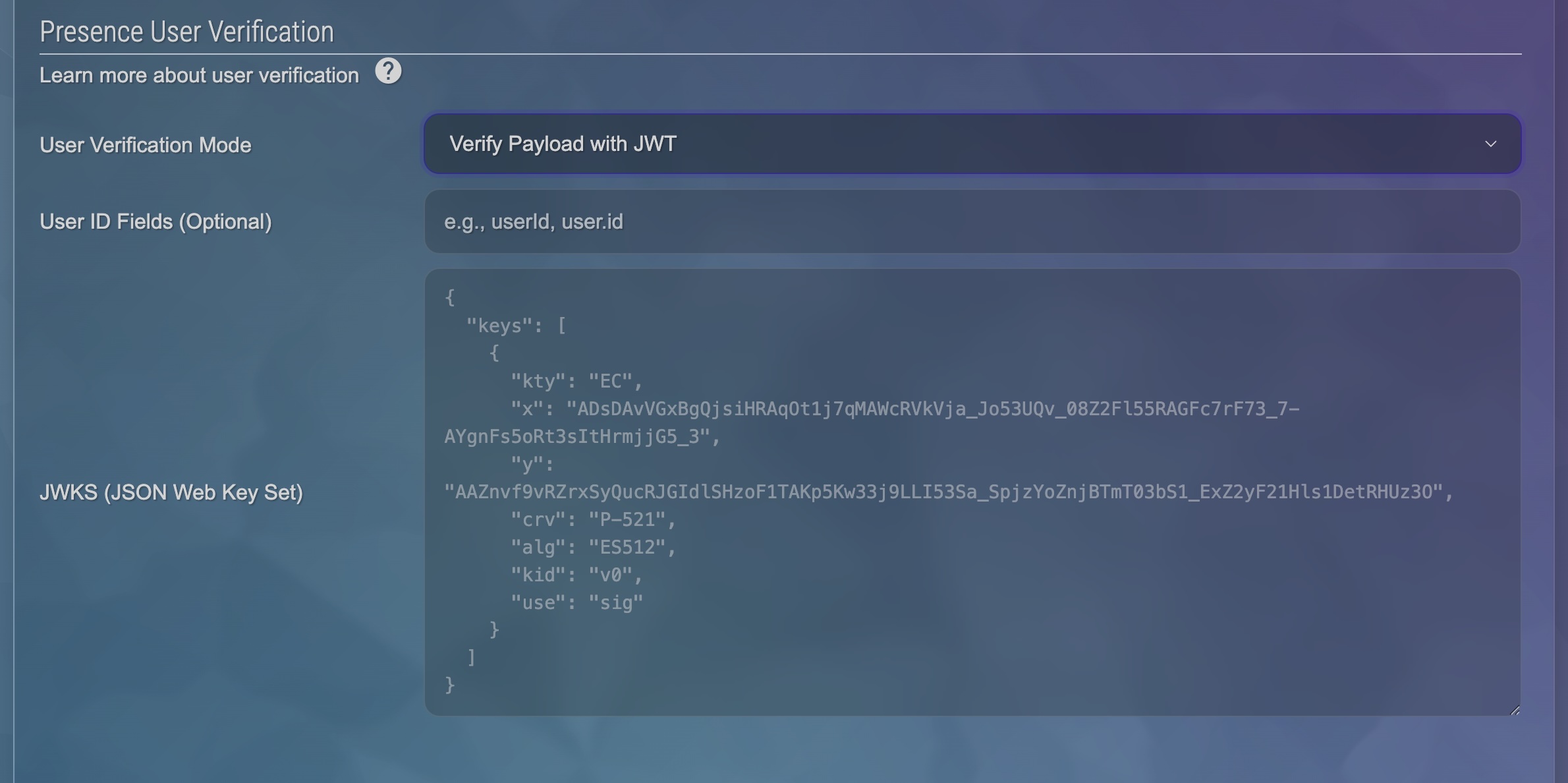
Implementation
Your backend must generate a signature or a JWT. The client then passes this credential in an `auth` object to the `join()` or `send()` methods in the SDK.
// --- Backend: Generate a JWT for the user ---
import jwt from 'jsonwebtoken';
const payload = {
sub: 'user-123', // The user's unique ID
name: 'Alice',
role: 'moderator'
};
const identityToken = jwt.sign(payload, PRIVATE_KEY, { algorithm: 'RS256' });
// --- In Your Client-Side SDK ---
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
const nls = new NonLocalStorage(credentials, 'private-room-456');
const auth = { identityToken };
// Authenticate when joining the room
await nls.join({ id: 'user-123', name: 'Alice', customData: 'some-value' }, auth);
// AND authenticate when sending a message
await nls.send({ type: 'chat', text: 'Hello world!', userId: 'user-123' }, { auth });Automatic At-Rest Encryption
What It Is
An additional layer of server-side encryption. Data values are symmetrically encrypted on the Vaultrice server before being stored, preventing plaintext access in the database. This adds an extra layer of protection against a direct breach of the underlying database infrastructure.
Best For
Applications storing sensitive but non-critical data that need an extra layer of server-side protection, such as user preferences or internal application state.
Configuration
In your project's "Classes" settings within the Management UI, enable the "Additional At-Rest Encryption" checkbox for the desired class.

Implementation
No code changes are needed in your SDK. The encryption and decryption are handled automatically and transparently on the server side.
Atomic Operations
Server-side atomic mutators (for example nls.incrementItem, nls.decrementItem, nls.push, nls.splice, nls.merge, nls.setIn and other collection/object mutators) operate on plaintext on the Vaultrice server. They are therefore not end-to-end encrypted — the server must be able to decrypt values to perform the operation.
This is a standard trade-off: Additional At-Rest encryption provides extra server-side protection but the server can still read/modify values to support atomic/collaborative features. If you require end‑to‑end secrecy, do not rely on server-side atomic mutators; instead implement atomic logic on the client while using E2EE, or use an unencrypted class when you need server-side atomic operations.
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
// If SF 3 is enabled in the UI for the 'encrypted-user-data' class,
// data is automatically encrypted with an additional layer on the server.
const userPrefs = new NonLocalStorage(credentials, {
id: 'user-preferences-123',
class: 'encrypted-user-data' // The class configured for At-Rest Encryption
});
// This data is encrypted transparently - no changes to your code needed
await userPrefs.setItem('theme', 'dark');
await userPrefs.setItem('api_tokens', 'sensitive-token');End-to-End (E2EE) Encryption
What It Is
The highest level of data confidentiality. Data is encrypted directly on the user's device using a passphrase and can never be read by the server. This is the highest level of confidentiality, ensuring that no one—not even Vaultrice—can read the content of your data.
Best For
Applications handling highly sensitive, private, or regulated data like private messages, financial data, or health information.
Configuration
In the "Classes" settings, you can define the e2ee salt length. This sets the default byte length for the salt used in key derivation. You can also trigger key rotation to force all connected clients to rotate their keys.

Implementation
Enable E2EE by providing a passphrase during SDK initialization. Before the first operation, call getEncryptionSettings(). The SDK fetches a unique salt from the server to derive the encryption key.
Atomic Operations
Server-side atomic mutators (for example nls.incrementItem, nls.decrementItem, nls.push, nls.splice, nls.merge, nls.setIn and other collection/object mutators) are fundamentally incompatible with end-to-end encryption. The server cannot decrypt E2EE data and therefore cannot perform atomic read-modify-write operations on it.
This is intentional: E2EE preserves a "zero-knowledge" model where only clients with the passphrase can read or modify plaintext. Choose E2EE for maximum privacy and implement any complex or atomic state changes on the client, or choose an unencrypted class when you need server-side atomic/collaborative features.
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
const nls = new NonLocalStorage(credentials, {
id: 'my-secret-journal',
passphrase: 'a-very-strong-and-secret-passphrase'
});
// Fetch initial settings. This can override the default salt length.
// If saltLength is omitted, the project's configured e2eSaltLength is used.
await nls.getEncryptionSettings({ saltLength: 16 });
// This value is encrypted on YOUR device before being sent to Vaultrice.
// Even Vaultrice cannot decrypt this data without the passphrase.
await nls.setItem('diary_entry_1', 'This is a top secret message.');
await nls.setItem('financial_data', { account: '***', balance: 50000 });SDK Authentication Methods
Vaultrice supports flexible authentication to fit different architectures and security requirements.
Choose the method that matches your risk profile and infrastructure.
Direct Authentication
apiKey + apiSecretSimplest setup. SDK manages tokens for you.
Secrets are present in client code.
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
const nls = new NonLocalStorage({
projectId: 'your-project-id',
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
apiSecret: 'your-api-secret'
}, 'your-object-id');Backend-Issued Access Token
accessToken / getAccessToken()Backend generates a temporary token.
No secrets in client. Maximum secret protection.
// Backend: Generate token
import { retrieveAccessToken } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
async function generateTokenForClient() {
const accessToken = await retrieveAccessToken(
'your-project-id',
'your-api-key',
'your-api-secret'
);
return { accessToken };
}
// Backend: and prepare an endpoint that returns it
app.get('/api/vaultrice-token', async (req, res) => {
const accessToken = await generateTokenForClient();
res.json({ accessToken });
});
retrieveAccessToken(projectId, apiKey, apiSecret, { origin: req.headers.origin })) when minting tokens on your backend. Otherwise, token retrieval will fail.Choose between manual or automatic token refresh for your client integration.
Manual refresh | Automatic refresh
🔑Backend-Issued Access Token: Client Integration
Wired Access Token (Manual)
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
const { accessToken } = await fetch('/api/vaultrice-token').then(r => r.json());
const nls = new NonLocalStorage({
projectId: 'your-project-id',
accessToken
}, 'your-object-id');
// When the token is about to expire:
nls.onAccessTokenExpiring(async () => {
console.log('Token is about to expire, fetching a new one...');
const { newAccessToken } = await fetchTokenFromMyBackend();
nls.useAccessToken(newAccessToken);
});Access Token Provider (Automatic)
import { NonLocalStorage } from '@vaultrice/sdk';
const nls = new NonLocalStorage({
projectId: 'your-project-id',
getAccessToken: async () => {
const r = await fetch('/api/vaultrice-token')
if (!r.ok) throw new Error('Failed to fetch token')
const { accessToken } = await r.json()
return accessToken
}
})getAccessToken() automatically when needed. No manual refresh required.Choosing an Approach
| Method | Option | Token Refresh | Secrets in Client? | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Authentication | apiKey + apiSecret | Automatic | Yes | Quick setup, prototypes, client-heavy apps with Origin Restriction |
| Wired Access Token | accessToken | Manual | No | Client receives a token from backend; you handle refresh. Good when you don't want secrets in the client. |
| Access Token Provider | getAccessToken() | Automatic | No | Best for production: SDK calls this async function when it needs a fresh token. Centralized control, no secrets in client. |
